Recently, I decided to explore infrastructure concepts more deeply and set up a personal learning environment. To build the environment, I used my MacBook Pro 2021 with Docker without access to additional hardware. The initial setup went smoothly.
Installing GitLab
The M1 chip in MacBooks uses the ARM architecture, so I used the yrzr/gitlab-ce-arm64v8:latest Docker image.
Create Required Directories
First, create three working directories for GitLab: etc, log, and opt. Otherwise, errors will occur. Modify the volumes section in the Docker Compose configuration to point to these directories. Two ports, 9922 and 9980, are exposed. Since this setup is for local use, 443 is not enabled.
|
|
Note: Exposing port 9980 avoids issues like this one.
Update GitLab Configuration
Once the container is running, modify the GitLab configuration file:
|
|
Add the following lines at the end:
|
|
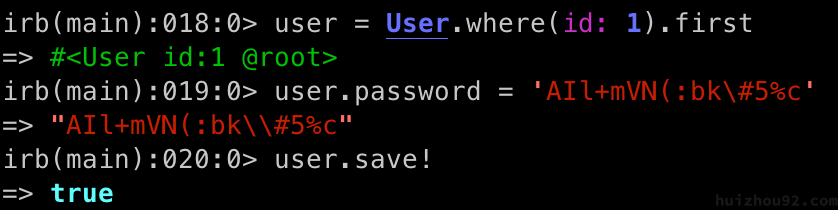
Change the Default Password
Run the following commands to update the root password:
|
|
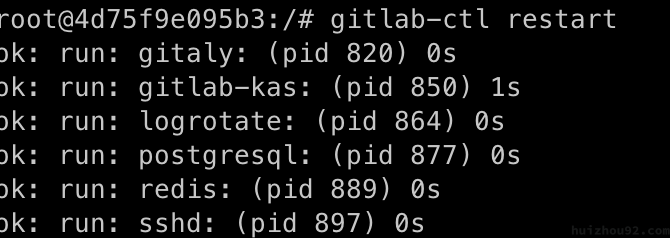
Finally, reconfigure and restart GitLab:
|
|
Access GitLab
Visit http://127.0.0.1:9980 in your browser. The default root username and the password you just set should work.
Adding SSH
To enable SSH-based access like GitHub, create an SSH key pair and add the public key to GitLab, and update your local SSH configuration in ~/.ssh/config:
|
|
Test the connection:
|
|
You should see:
|
|
Create a new project and clone it
|
|
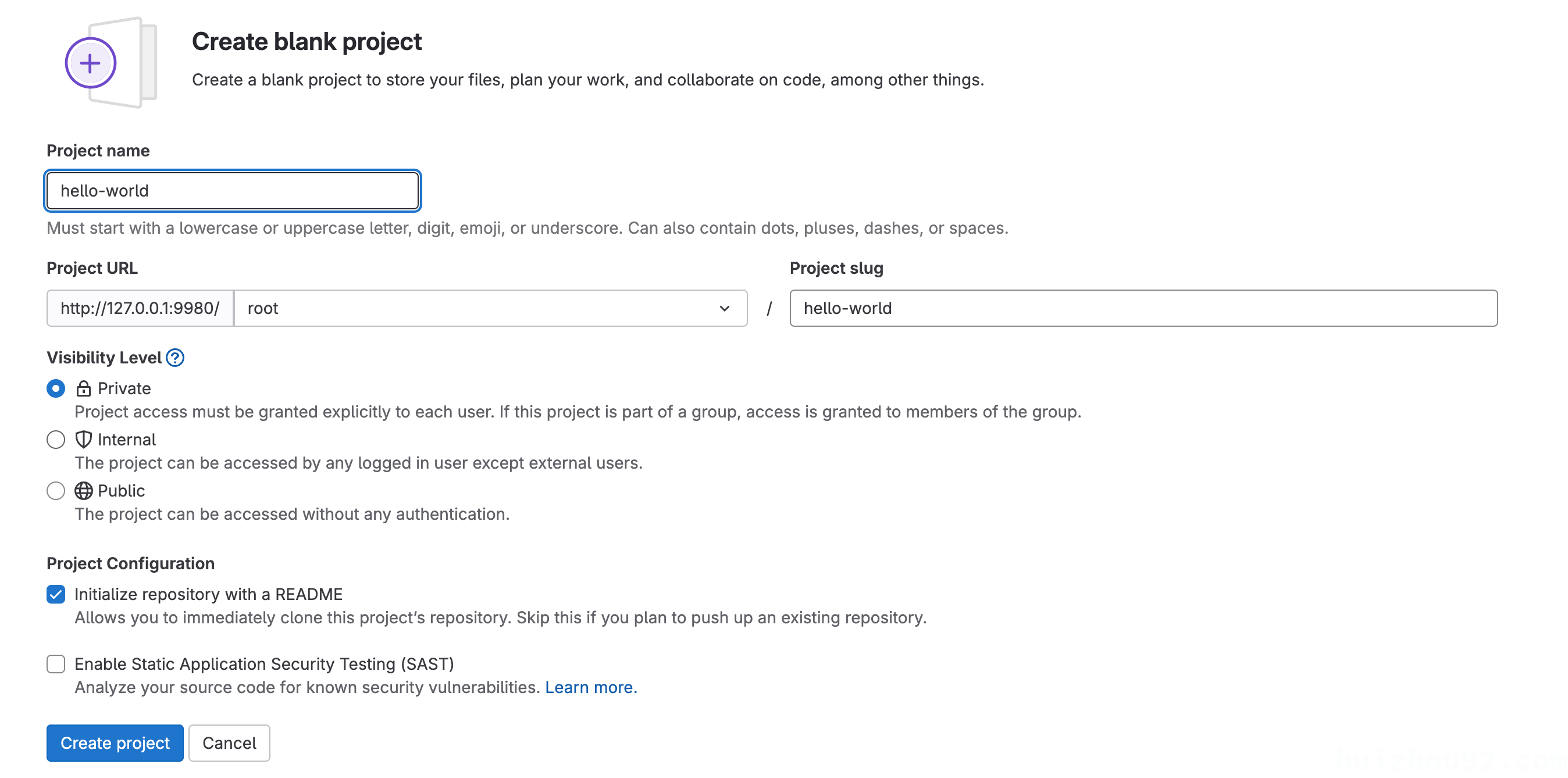
|
|
Configuring GitLab Runners
Go to Settings -> CI/CD -> Runners, and follow the instructions under “Show runner installation and registration instructions.”
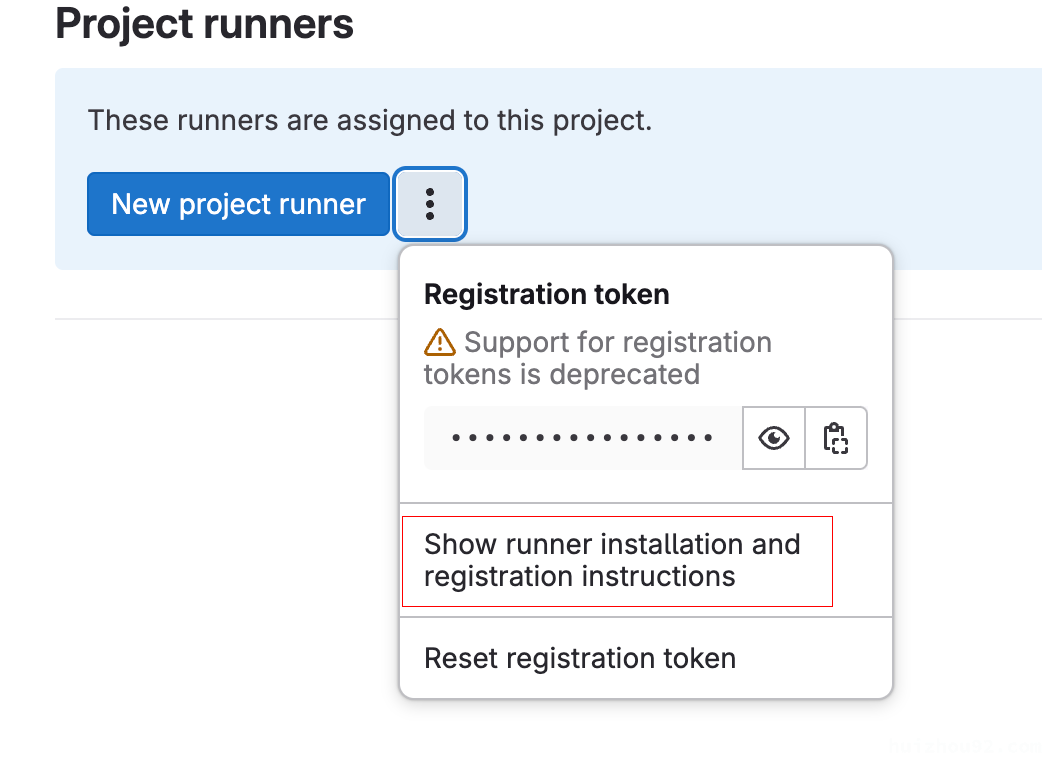
Install and Register the Runner
|
|
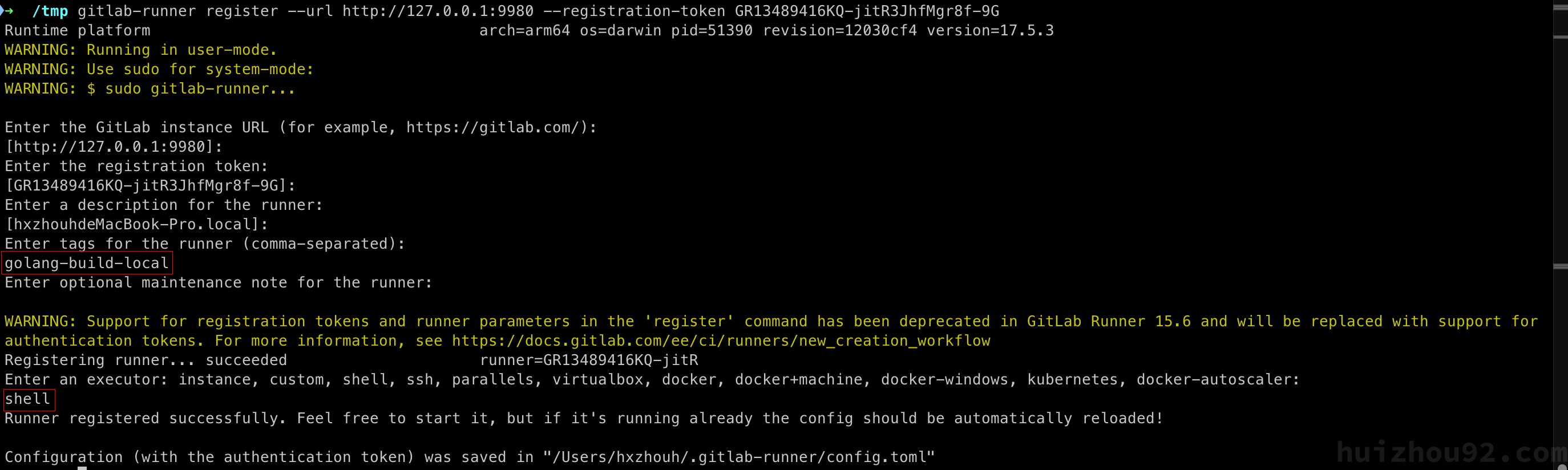
Key Points:
- Tags: Use tags to specify runner tasks in
.gitlab-ci.yml. - Executor: For this example, use the
shellexecutor.
For more information about GitLab Runner, please refer to the article on the official website, which will not be expanded here.
Testing CI/CD Pipeline
Create a .gitlab-ci.yml file in your project:
|
|
Push the code to GitLab, and the build pipeline should execute automatically.

Artifacts can be found at:
|
|

Next Steps
This setup concludes the local GitLab environment. In the next article, I’ll demonstrate setting up a local Kubernetes cluster and automating Docker image deployment from GitLab to Kubernetes for a complete CI/CD pipeline.
